
Overview
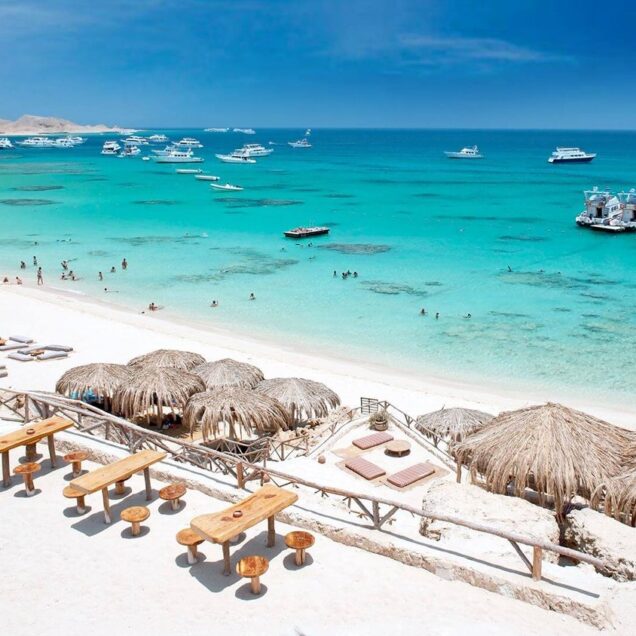
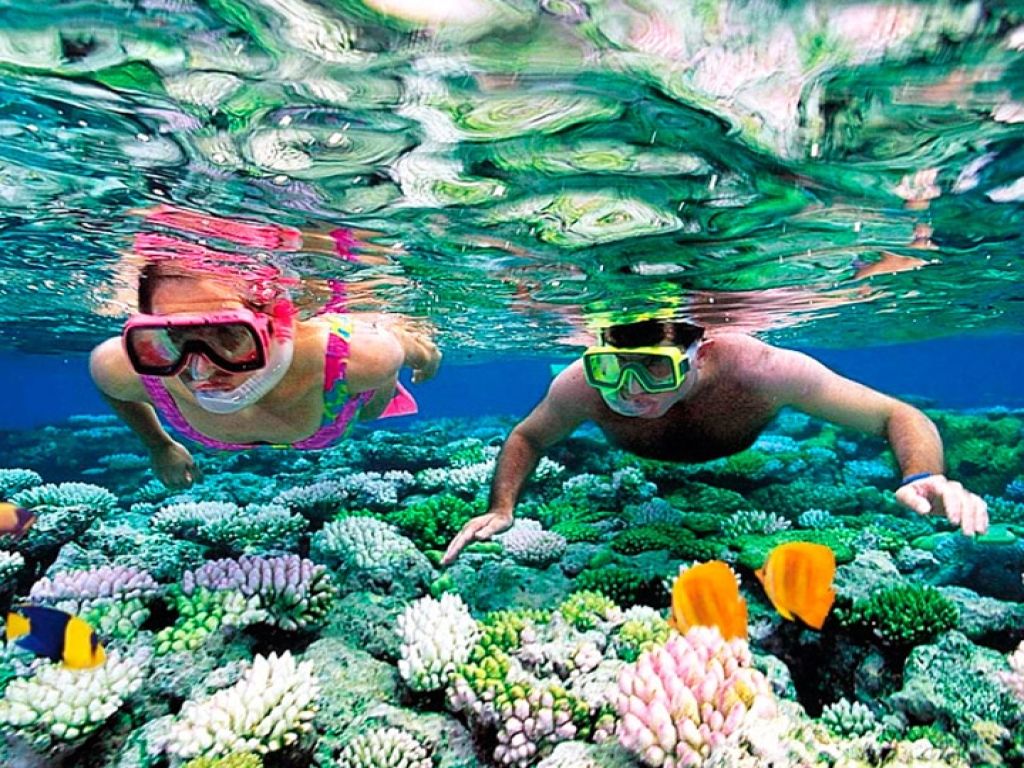
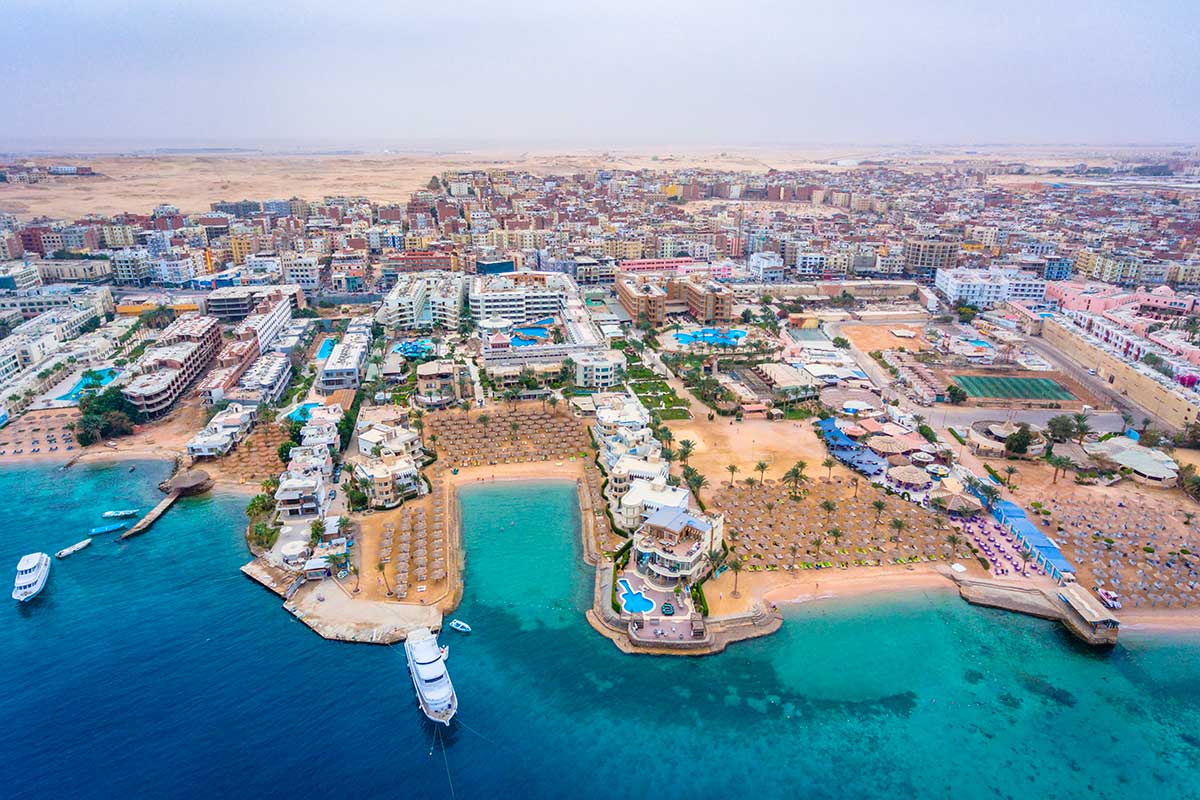
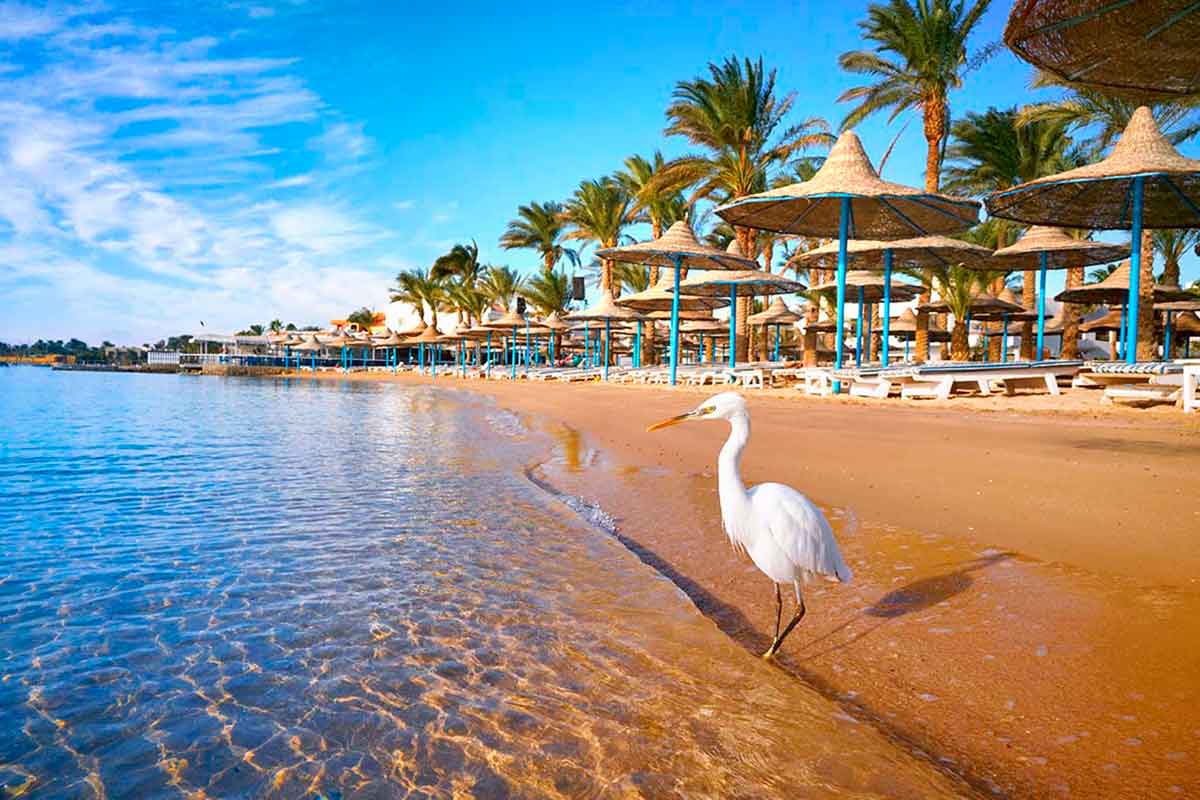
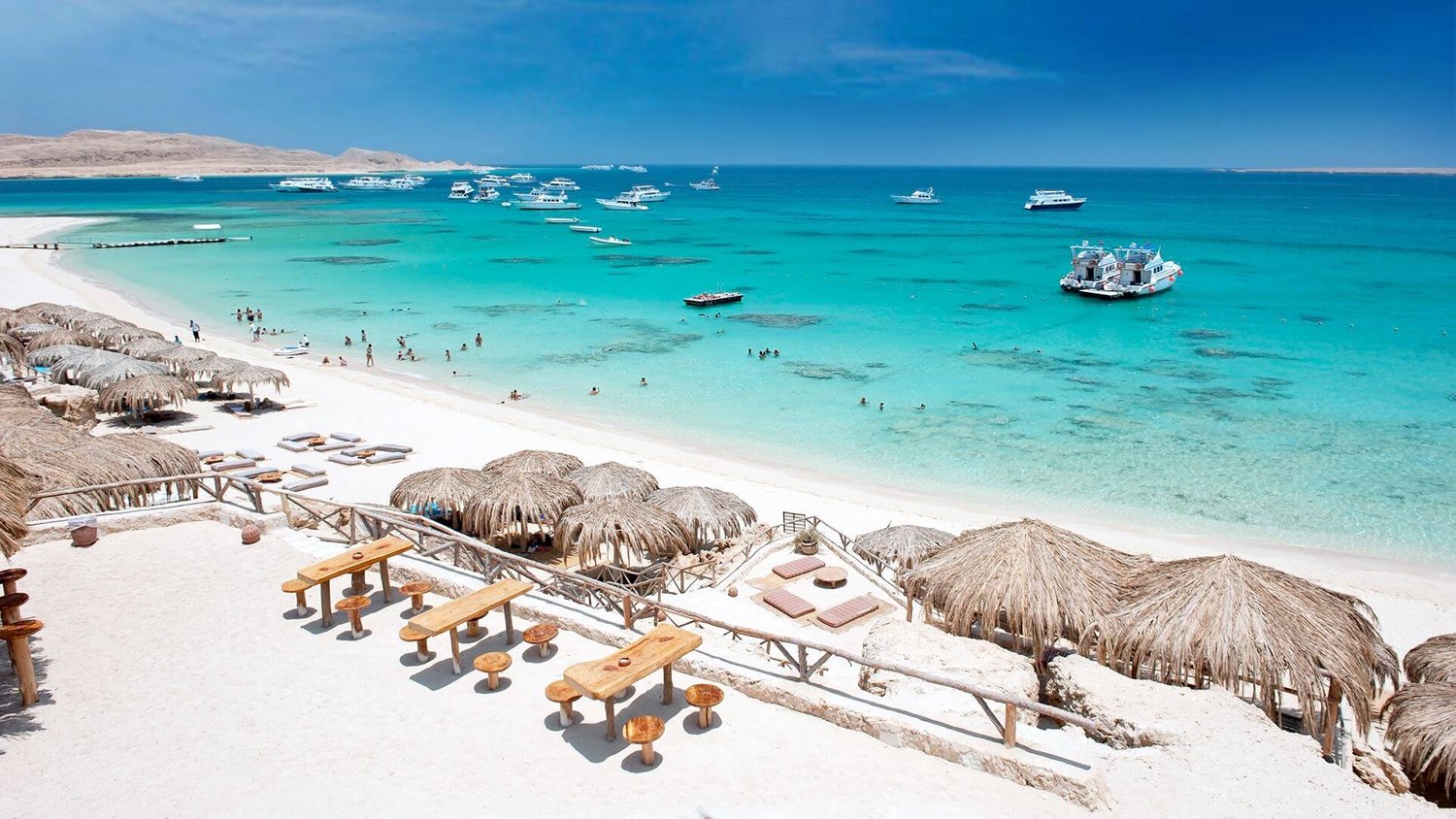
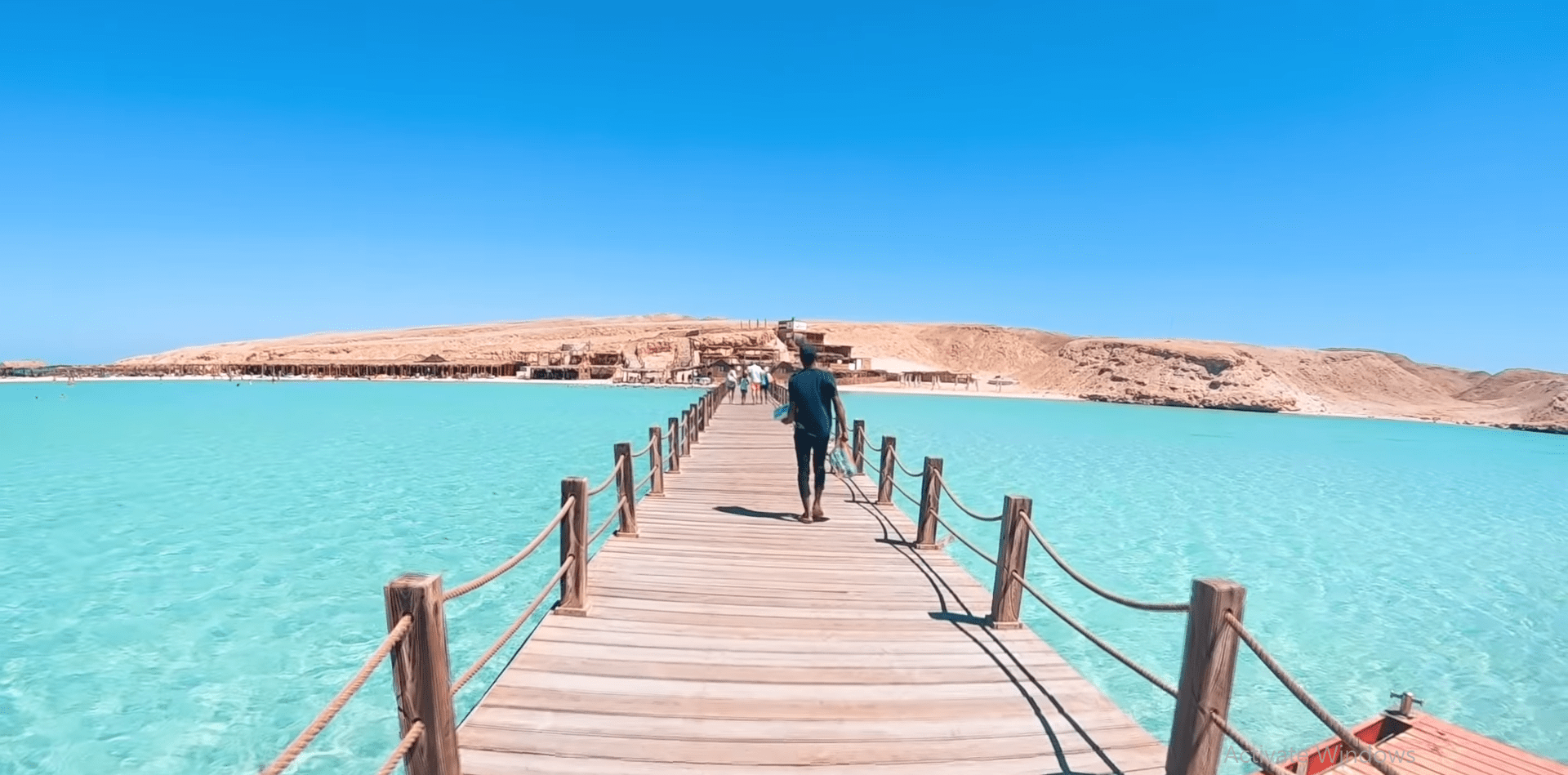
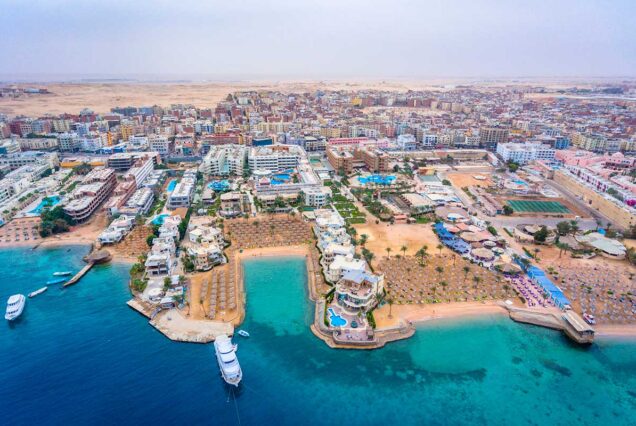
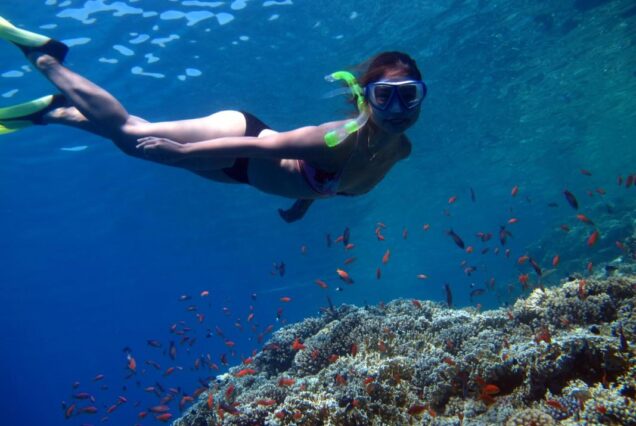
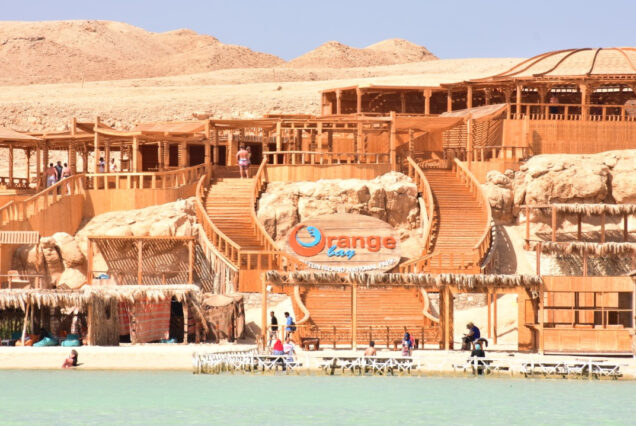
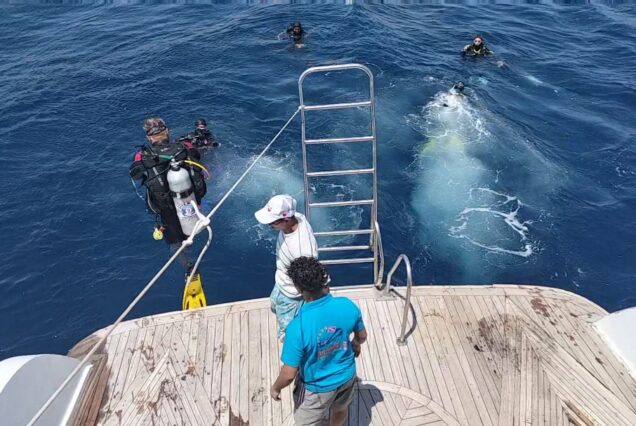
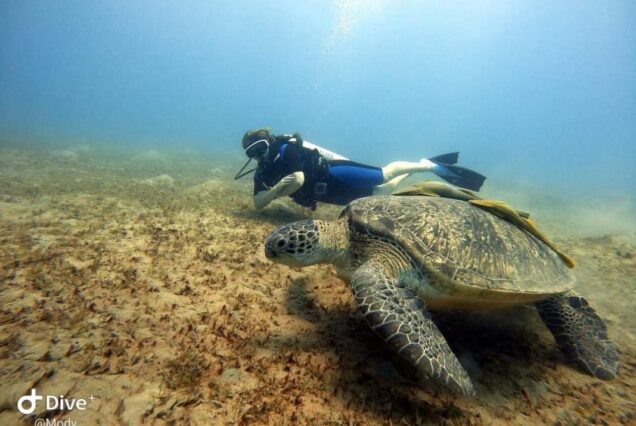
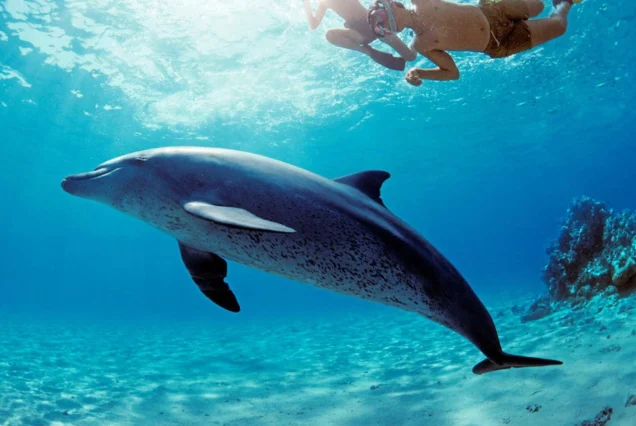
Hurghada was founded in the early 20th century. For many decades it was a small fishing village, but it has grown into a major Red Sea resort as a result of Egyptian and foreign investment that began in the 1980s. Holiday resorts and hotels provide facilities for windsurfing, kitesurfing, yachting, scuba diving and snorkeling. The city is known for its watersports, nightlife and warm weather. Daytime temperatures are around 35 °C (95 °F) most of the year, and during July and August temperatures can reach over 46 °C (115 °F). Hurghada is a popular holiday destination for Europeans, especially during the winter, and some spend Christmas and New Year there. Hurghada extends for about 36 kilometres (22 mi) along the coast, but does not reach far into the surrounding desert. The resort is a destination for Egyptian tourists from Cairo, the Delta and Upper Egypt, as well as package holiday tourists from Europe. Many of Hurghada's newer hotels, restaurants, and shops are located along El Mamsha. Most of the largest hotel resorts are located in the area between Mamsha and Sahl Hasheesh on El Mamsha. Beyond Sahl Hasheesh there are the hotels of Makadi Bay. Dahar is the oldest part of the town, where the traditional bazaar, post office and long-distance bus stations (Go Bus and Upper Egypt Bus) are situated. The busiest area is Sakala, the city center on Sheraton Road lined with hotels, shops and restaurants.Sights
Map
Info
The Egyptian Red Sea coast has been inhabited since antiquity, with the area of Hurghada being occupied since the 4th century, when the ancient settlement of Abu Sha’ar (Arabic: ابو شعر), located 20 km north of the modern city, was established. Originally founded as a Roman military fort for Ala Nova Maximiana unit between 309-311, it was transformed into a Christian community around 400. The Christians repurposed the fort into a church, leaving behind inscriptions, graffiti, and artifacts such as a 5th-century papyrus and a tapestry with a cross. The settlement declined after either the Sasanian or Arab conquest of Egypt.[5]






























